The aerospace industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by record demand for commercial jets, defence programmes and space exploration. To seize this opportunity, suppliers must find ways to ramp up output without compromising quality, innovation, or cost. By Will Stirling
The biggest hurdle facing the aerospace industry is how to scale up production. Airlines are investing heavily in new fleets, governments are increasing spending on advanced defence systems, and private companies are pushing the frontiers of space exploration and satellite technology. While this growth is a welcome rebound after years of turbulence, it has exposed bottlenecks in the supply chain, exacerbated by rising operational costs, material shortages and evolving regulatory requirements.
Nowhere is this challenge clearer than in the commercial aircraft backlog, which has ballooned to nearly 16,000 planes – valued at more than £250bn for the UK alone. At current production rates, clearing this backlog could take over a decade. Meanwhile, demand continues to climb as airlines place hundreds of new orders yearly.
Yet, this pressure brings opportunity. “The fact I can’t name another industry with a 10-year-plus backlog worth over US$1.5 trillion globally shows just how massive the growth trend is,” says Balaji Srimoolanathan, Director for Aerospace, Space and the Aerospace Growth Partnership at ADS.
“The primes and top tiers are diversifying their suppliers, sustainability is becoming ever-more critical, and new technologies are accessible and affordable. There is more business to be won by a greater number of suppliers than ever before, adding up to more opportunities, particularly for those with the right tools and technologies in place.”
Srimoolanathan explains that the key to unlocking these opportunities lies in integrating advanced capabilities, such as intelligent manufacturing systems, into today’s production processes. This move has been proven to drive greater efficiency and agility without comprising stringent quality standards.
Digital Innovation in Action
As production ramps up, shortages of critical components like semiconductors, electronics and raw materials like aluminium and titanium continue to cause delays. The pandemic’s ripple effects are still being felt, slowing assembly lines and affecting deliveries. Even seemingly minor components, such as fasteners, are in short supply.
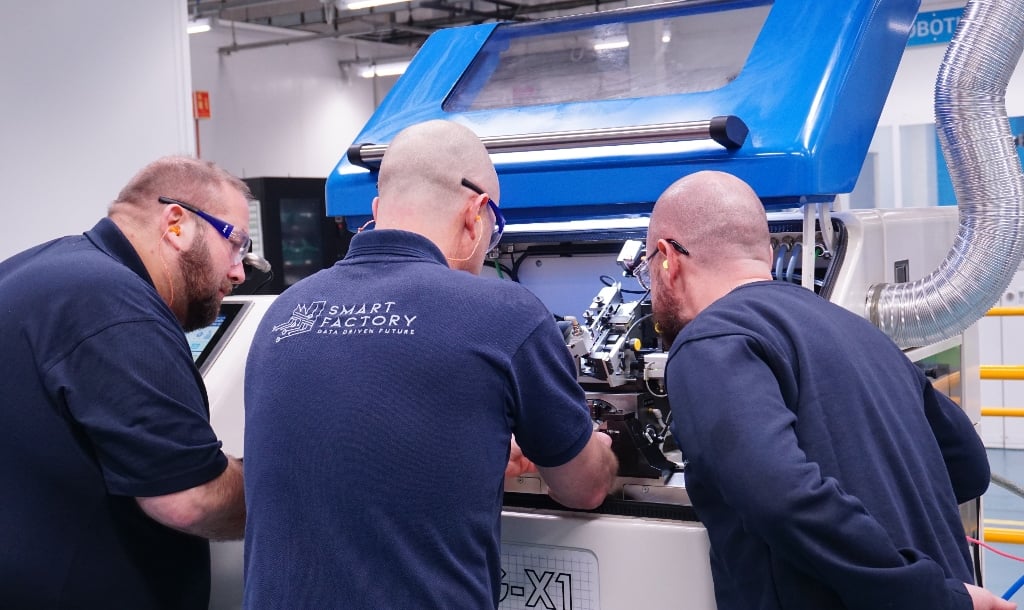
Recognising this, LISI Aerospace partnered with the University of Sheffield Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC) to explore how digital tools can drive process improvements. Together, they developed a cutting-edge smart production line at LISI’s Rugby facility.
The pilot line integrates five connected factory machines, each handling a distinct process. Key innovations include sensor data and data analytics to predict component quality, alongside an expanded apprenticeship programme to support new roles like software developers and data analysts.
The result is a more than 100% performance improvement, enabling the Rugby site to hit record turnover and win additional contracts worth over £2m. The project also spurred a dedicated process development department, created a dozen new jobs and paved the way for a further £6.5m investment to implement two more connected production lines by 2027.
An AMRC spokesperson said the project demonstrates how industrial digital technologies can transform operations. The success has ‘set a new benchmark for fastener production processes’ and clearly shows the potential of technology-driven innovation in aerospace.
Process Improvements Within Constraints
While LISI’s collaboration showcases the benefits of innovation, industry-wide progress is often hampered by a reliance on established processes and materials. “The industry is built on aircraft and parts certified to specific production techniques, many of which were designed decades ago,” explains Andrew Mair, Chief Executive of the Midlands Aerospace Alliance (MAA).
While this reliance on legacy methods may limit flexibility in core manufacturing processes, there’s significant scope for improvements in areas that run parallel to assembly. Upgrading to integrated software platforms for production planning, resource management and inventory tracking, for example, is an area where many smaller manufacturers lag, yet can unlock substantial efficiency gains. Similarly, using robotics and automation to move materials or load machines can streamline operations and reduce manual labour and downtime.

Design innovations also hold promise. Advances in simulation and digital twin technologies allow suppliers to optimise components and assemblies before physical production, compressing design cycles and identifying potential issues earlier.
Generative design, where AI-driven software explores thousands of potential configurations, is helping create lighter, stronger, more cost-efficient components. Combined with additive manufacturing, suppliers can prototype and produce highly complex parts faster and, importantly, with significantly less waste than traditional ‘subtractive’ machining.
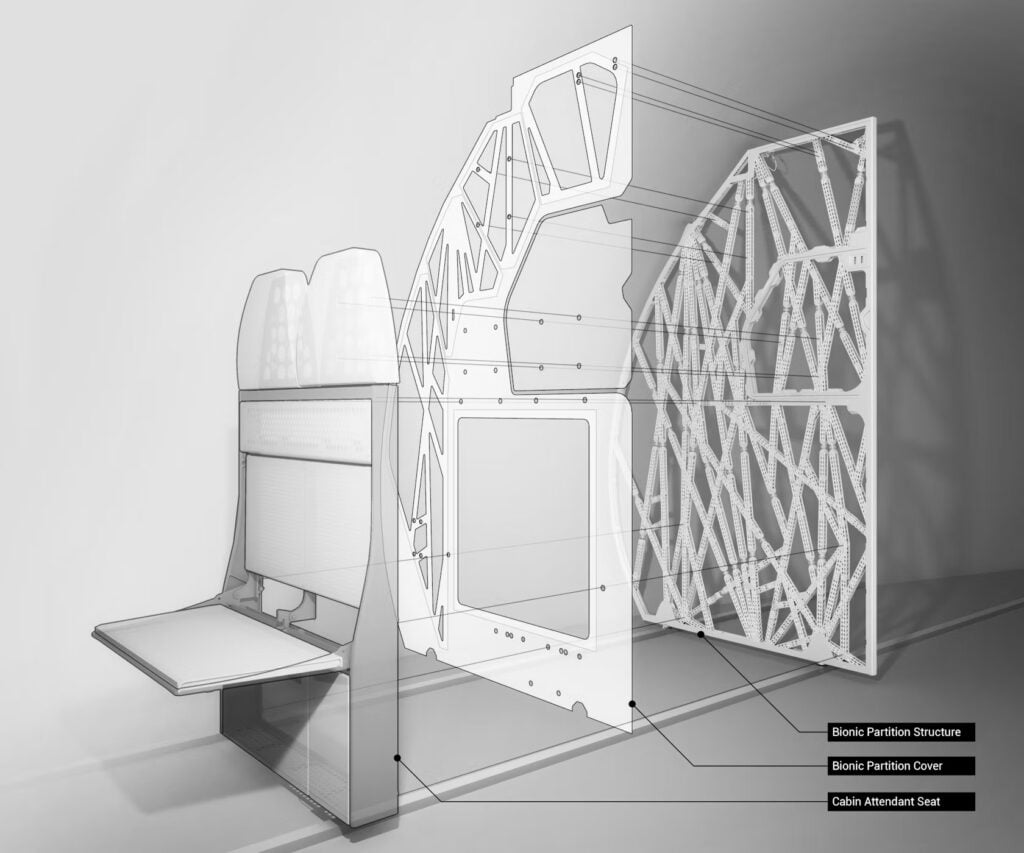
For instance, Airbus and Autodesk have used generative design and additive manufacturing to produce the world’s largest 3D-printed cabin component. Inspired by cellular structures and bone growth, the latticed partition to separate the passenger cabin from the galley is structurally as strong as conventional designs but 45% (30kg) lighter. When scaled to the entire cabin, Airbus estimates that the new design approach could save up to 465,000 metric tonnes of CO2 emissions a year.
Government Backing Fuels Further Investment
Recognising the transformative potential of advanced technologies, recent government announcements are geared towards accelerating adoption. One such initiative is the expansion of Made Smarter, an industry-government programme aimed at helping SME manufacturers adopt technology and build digital skills. Since its 2019 launch in the North West, Made Smarter has engaged with 2,500 manufacturers, funded over 330 technology projects, created more than 1,500 jobs and upskilled nearly 2,800 workers.
Its upcoming national rollout to all nine English regions by 2025/26, followed by Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland in 2026/27, will extend those benefits to thousands of manufacturers across the UK.
“The programme has proven the value technology and digital skills can bring,” says Donna Edwards, Director of Made Smarter NW, who described the national roll-out as “a huge vote of confidence in the contribution SMEs make to UK manufacturing.”
Additionally, the government’s announcement of £975m to extend the Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI) programme to 2030 was welcomed – although many favoured a longer-term commitment. With matching industry contributions, the funding will exceed £2bn, providing critical support for ultra-efficient and zero-carbon technologies.
“This support for R&D is crucial at a time the sector is ramping up rates to meet today’s demand while delivering ambitious technology programmes to bring next-generation aircraft technologies to reality,” says Gary Elliott, CEO of ATI.
Plotting a Sustainable Flight Path
The UK is making significant strides in sustainable aviation. The latest development saw a new Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) mandate come into force on New Year’s Day. The mandate requires that 2% of UK jet fuel demand be met by SAF, rising to 10% by 2030 and 22% by 2040—delivering up to 6.3 megatons of carbon savings annually.
The mandate will be bolstered by the introduction of a revenue certainty mechanism to de-risk investments in new SAF plants and provide the confidence needed to scale domestic production.
The potential of hydrogen-powered aviation is also gaining momentum, with Russ Dunn, GKN Aerospace CTO, recently named as the new chair of the Hydrogen in Aviation Alliance. The HIA’s first major report, published in 2024, outlined a clear roadmap for industry and government to drive adoption. Yet, realising this vision requires more robust support for R&D, particularly within the manufacturing supply chain.
Andrew Mair explains that nearly all the R&D support currently goes to large corporations or start-ups, leaving the existing supply chain underserved. “We need more regionalised support, particularly for clusters like the Midlands Aerospace Alliance, to ensure small companies get the backing they need.”
Srimoolanathan of ADS underscores that aerospace is uniquely positioned to deliver immediate and long-term benefits for the UK economy. “The backlog presents an opportunity for short-term growth, job creation and technological advancement,” he says.
“But this hinges on balancing the immediate demands of today with strategic investments in areas like zero-emission technologies. With sustained support, the UK can maintain its position as a global aerospace leader while delivering tangible economic and environmental benefits.”
Subscribe to the MTDCNC Newsletter
Subscribe to our Newsletter today!
Stay up to date with the latest industry news and events.